Have you ever wondered if the popular keto diet is a good choice for those with hypothyroidism? Well, today we’re going to dive into this topic and explore the risks of following a keto diet if you have an underactive thyroid. So, if you’re someone who is interested in weight loss and improving your health, stick around because you’re going to learn more about the potential dangers of the keto diet for hypothyroidism.
When it comes to hypothyroidism, it’s important to approach any diet plan with caution. The keto diet, which is high in fats and low in carbs, can potentially impact the functioning of your thyroid gland. The main issue lies in the fact that the thyroid gland relies on glucose as its primary fuel source. With the drastic reduction in carbohydrates on a keto diet, your body enters a state of ketosis, where it starts producing ketones for energy. This shift from glucose to ketones may hinder the production of thyroid hormones, leading to an imbalance in the body. However, it’s important to note that every individual is different, and while some may experience adverse effects, others may not be affected at all. In our upcoming article, we’ll delve deeper into the risks and potential alternatives for those with hypothyroidism who are considering the keto diet. So, stay tuned and get ready to discover how you can make informed decisions about your diet and health.
Understanding Hypothyroidism
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, resulting in insufficient production of thyroid hormones. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. When the thyroid gland fails to produce enough thyroid hormones, it can lead to a wide range of symptoms and health issues.
Causes of hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism can have various causes, including autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland. Other causes may include radiation therapy, iodine deficiency, certain medications, and congenital issues.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism
The symptoms of hypothyroidism can vary from person to person, but common signs include fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, dry skin, hair loss, and muscle aches. Additionally, individuals with hypothyroidism may experience depression, memory problems, and a decreased ability to concentrate.
Introduction to the Keto Diet
What is the keto diet?
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that has gained significant popularity in recent years. The main goal of the keto diet is to shift the body’s primary source of fuel from glucose (derived from carbohydrates) to ketones (produced by the liver from stored fat). This metabolic state is known as ketosis and is believed to have numerous health benefits.
How does the keto diet work?
When you restrict your carbohydrate intake on the keto diet, your body begins to burn stored fat for energy instead of glucose. This shift in fuel source promotes weight loss and can also lead to improved insulin sensitivity. By reducing carbohydrate intake to a minimal level, the body is forced to utilize its fat stores, resulting in a gradual reduction in body weight.
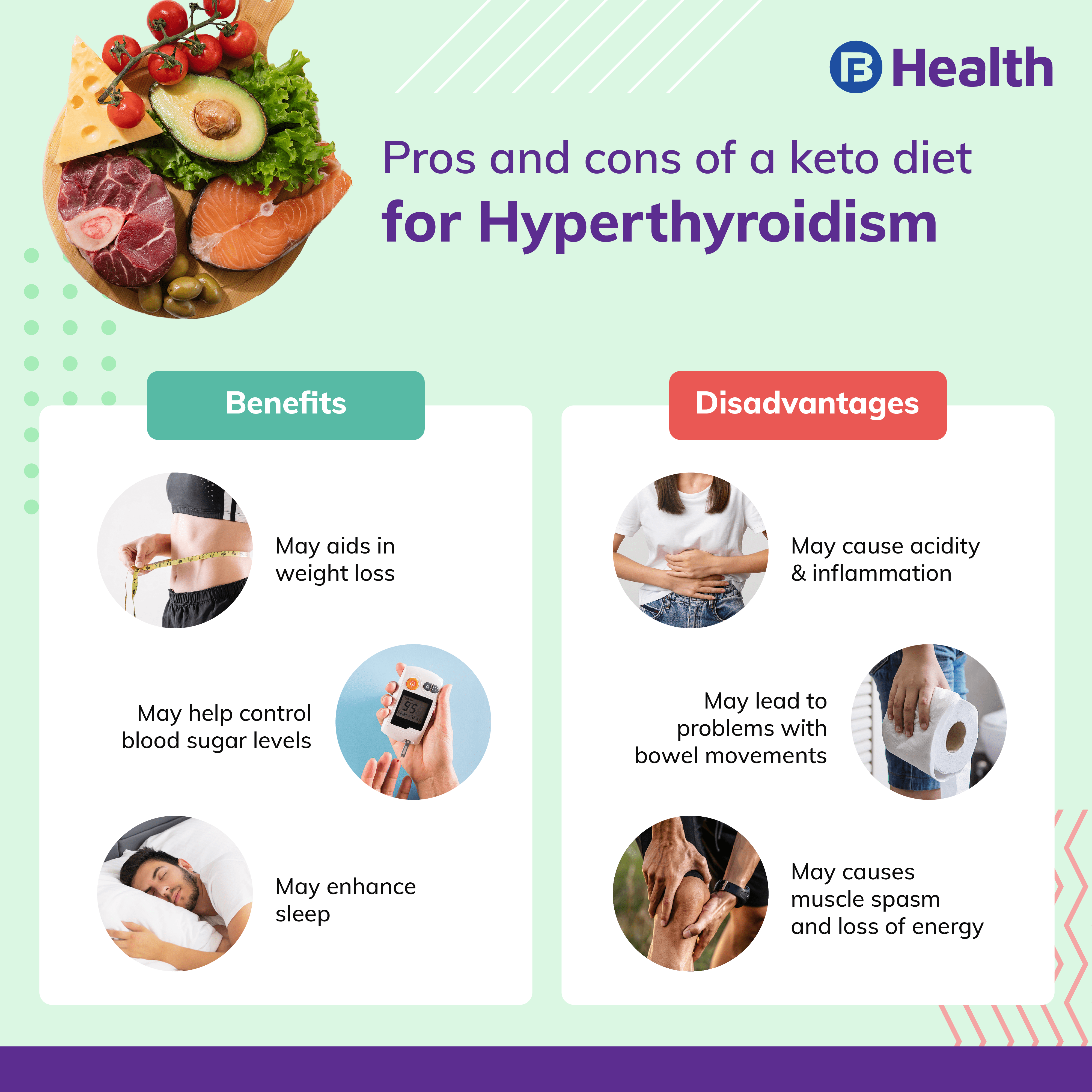
Benefits of the keto diet
Proponents of the keto diet claim that it can lead to significant weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and increased energy levels. Additionally, some studies suggest that the keto diet may have potential benefits for certain conditions, such as epilepsy and some neurodegenerative disorders.
Effects of the Keto Diet on Hypothyroidism
Interference with thyroid hormone production
One of the concerns regarding the keto diet’s impact on hypothyroidism is its potential interference with thyroid hormone production. The production of thyroid hormones, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), requires an adequate supply of dietary iodine, which is predominantly found in carbohydrate-rich foods. By severely limiting carbohydrate intake, individuals on the keto diet may inadvertently reduce their iodine intake, potentially affecting thyroid hormone synthesis.
Impact on metabolism
Another potential risk of the keto diet for individuals with hypothyroidism is its impact on metabolism. Hypothyroidism already slows down the body’s metabolic rate, leading to difficulties in weight management. The keto diet, with its restrictive nature, may further slow down metabolism, making it even more challenging for individuals with hypothyroidism to lose weight.
Potential exacerbation of hypothyroid symptoms
Individuals with hypothyroidism often struggle with fatigue, depression, and brain fog, among other symptoms. While the keto diet has been praised for its potential to increase energy levels and improve mental clarity, the restrictive nature of the diet may pose challenges for those with hypothyroidism. The abrupt reduction in carbohydrate intake can worsen fatigue and mood disturbances, making it important to carefully consider the potential effects on hypothyroid symptoms.
Reduced Carbohydrate Intake and Thyroid Function
The role of carbohydrates in thyroid regulation
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in thyroid hormone regulation. When carbohydrate intake is limited, the body responds by decreasing the production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which triggers the release of T3 and T4. This decrease in TSH production can ultimately lead to a reduction in total thyroid hormone levels, potentially contributing to the development or worsening of hypothyroidism.
Effect of low-carb diets on thyroid hormone levels
Several studies have examined the impact of low-carbohydrate diets, such as the keto diet, on thyroid hormone levels. While some studies have suggested that low-carbohydrate diets may lead to a decrease in T3 levels, others have found no significant changes. However, it is worth noting that these studies primarily focused on individuals with normal thyroid function, and more research is needed to understand the specific effects of the keto diet on individuals with hypothyroidism.
Studies on the relationship between the keto diet and hypothyroidism
Limited research has been conducted on the direct relationship between the keto diet and hypothyroidism. However, some studies have investigated the effects of low-carbohydrate diets on thyroid health in general. These studies have reported conflicting findings, with some suggesting that low-carbohydrate diets may negatively affect thyroid function, while others have found no significant impact. Further research is undoubtedly needed to determine the potential risks and benefits of the keto diet for individuals with hypothyroidism.

Implications for Weight Loss and Hypothyroidism
Challenges in losing weight with hypothyroidism
Weight loss can be particularly challenging for individuals with hypothyroidism. The slowed metabolism associated with hypothyroidism makes it harder for the body to burn calories efficiently, often leading to weight gain or difficulty in losing weight. This metabolic slowdown can make achieving weight loss goals more difficult, even with dietary interventions like the keto diet.
Impact of the keto diet on weight loss with hypothyroidism
While the keto diet has shown promising results for weight loss in some individuals, its effectiveness for individuals with hypothyroidism may vary. The restrictive nature of the keto diet may make it harder for individuals with hypothyroidism to sustain long-term weight loss due to the challenges in maintaining ketosis and the potential exacerbation of hypothyroid symptoms.
Considerations for individuals with hypothyroidism on the keto diet
If you have hypothyroidism and are considering the keto diet, there are several important considerations to keep in mind. It is crucial to monitor your symptoms and consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet. Additionally, working with a registered dietitian who specializes in thyroid health can help you create a customized meal plan that takes into account your unique needs and any potential risks associated with the keto diet.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Nutrient deficiencies
The keto diet’s restrictive nature may increase the risk of nutrient deficiencies, particularly if not carefully planned and monitored. Since the diet limits many fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, individuals may be at a higher risk of inadequate intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. This can be of concern for individuals with hypothyroidism, as adequate nutrient intake is crucial for supporting thyroid health and overall well-being.
Electrolyte imbalances
The keto diet can also disrupt the balance of electrolytes in the body, leading to potential imbalances. Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, play a vital role in maintaining proper bodily functions, including nerve and muscle function. Imbalances in electrolytes can cause symptoms such as muscle cramps, weakness, and irregular heartbeat. It is important to ensure adequate intake and monitoring of electrolyte levels while following the keto diet.
Increased cholesterol levels
The keto diet’s high-fat content, particularly from saturated fats, may lead to an increase in cholesterol levels for some individuals. Elevated cholesterol levels can increase the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular issues. This can be particularly concerning for those with hypothyroidism, as they may already be at a higher risk for heart-related complications.

Individual Variations and Response to the Keto Diet
Different thyroid conditions and responses to the keto diet
Individuals with different thyroid conditions may have varying responses to the keto diet. While some individuals with hypothyroidism may experience positive effects such as weight loss and increased energy, others may find that the diet exacerbates their symptoms or hampers their ability to lose weight. It is essential to listen to your body and work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the best dietary approach for your specific thyroid condition.
Monitoring thyroid function during the keto diet
If you decide to try the keto diet while managing hypothyroidism, it is crucial to regularly monitor your thyroid function to ensure optimal health. This can be done through blood tests that measure hormone levels, including TSH, T3, and T4. By closely monitoring your thyroid function, you and your healthcare provider can determine if any adjustments to your diet or medication regimen are necessary.
Consulting with a healthcare professional
Before making any significant changes to your diet, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or an endocrinologist who specializes in thyroid disorders. They can provide you with personalized guidance and help determine the most appropriate dietary approach for your specific needs and health goals.
Alternative Dietary Approaches for Hypothyroidism
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and gluten-free diet
For individuals with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition commonly associated with hypothyroidism, eliminating gluten from the diet may be beneficial. Some studies suggest that gluten may trigger an immune response in individuals with Hashimoto’s, leading to inflammation and further damage to the thyroid gland. Adopting a gluten-free diet may help reduce symptoms and support overall thyroid health in these individuals.
Balanced diet and nutrient intake
For individuals with hypothyroidism, maintaining a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods is essential. Focus on consuming adequate amounts of lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Incorporating a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help ensure sufficient nutrient intake to support thyroid function and overall well-being.
Customized meal plans for hypothyroidism
Working with a registered dietitian who specializes in thyroid health can be tremendously beneficial for individuals with hypothyroidism. They can help develop customized meal plans that address specific dietary needs, support thyroid function, and promote overall health and well-being. These meal plans may include a combination of nutrient-dense foods, portion control, and individualized recommendations tailored to your unique needs.

Conclusions and Recommendations
Summary of the risks and considerations
While the keto diet may offer weight loss benefits for some individuals, it is essential to consider the potential risks and considerations for individuals with hypothyroidism. The interference with thyroid hormone production, impact on metabolism, and potential exacerbation of hypothyroid symptoms are important factors to consider before embarking on the keto diet.
Importance of personalized approach
Due to the individual variations in thyroid conditions and responses to the keto diet, it is crucial to adopt a personalized approach. What may work for one person may not necessarily work for another, and taking into account individual needs and health goals is vital.
Consultation with a healthcare provider
Before starting any new diet or making significant dietary changes, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider, such as a registered dietitian or endocrinologist. They can provide personalized guidance, taking into account your specific thyroid condition, and help you make informed decisions about the most appropriate dietary approach for your overall health and well-being.
In conclusion, while the keto diet has gained popularity for its potential weight loss benefits, individuals with hypothyroidism should approach this diet with caution. The potential interference with thyroid hormone production, impact on metabolism, and exacerbation of hypothyroid symptoms raise concerns about its suitability for individuals with this condition. It is crucial to prioritize personalized guidance from healthcare professionals to ensure the best possible dietary approach for managing hypothyroidism effectively. Remember, your health is unique, and a customized approach is essential for optimal well-being.



